
Peter Griffin of the animated sitcom Family members Man winces in ache. He probably doesn’t have compartment syndrome, but need to most likely appear into the symptoms.
Shin ache is an more and more typical complaint between cross-nation skiers, creating a lot of lost days of skiing each and every 12 months. It’s hard to identify a single explanation for the trend, but better training demands, this kind of as high volumes of rollerskiing in the offseason, enhanced boot stiffness, diet programs that do not meet the caloric demands of instruction, or single-sport specialization from a youthful age may possibly play a part. In the person skier, nevertheless, a sports medicine physician can make a particular diagnosis, uncover the trigger of the dilemma, and then tailor a therapy strategy for the athlete.
The three most common causes of shin pain are shin splints, bony tension injuries and exertional compartment syndrome. The phrase ‘shin splints’ is typically incorrectly utilized to describe any shin pain in athletes. Even so, real shin splints are brought on by micro-tearing of the muscle away from the bone along the medial, or inner, element of the reduced shin. Soreness from shin splints is usually spread out along the inner shin, and typically goes away or ‘warms up’ with workout, but comes back right after exercise or following a difficult work out.

U.S. Olympian Kris Freeman for the duration of the four x ten k relay at 2009 Planet Championships in Liberec, Czech Republic. In the spring of 2009, Freeman had surgical treatment to remedy compartment syndrome in the two shins. (Photograph: Swix Sport)
In more superior situations, the pain can worsen during exercising, limiting a skier’s capability to race and train. Most athletes with shin splints are sore for the first handful of minutes of a ski, then the pain improves or disappears totally, and then they are sore again right after they great down.
Shin splints are typically diagnosed with no any unique testing, and can be managed properly with relative rest, stretching tight muscles, specially people of the calf, strengthening weak muscles, particularly individuals of the hips and ankles, and working on ski strategy and stability. A bodily therapist and sports medication doctor can operate with the skier to recognize underlying biomechanical concerns that could be causing their shin splints. An arch assistance orthotic might also be helpful.
A bony pressure injury is a far more serious problem, which occurs across a spectrum. Milder injuries cause some inflammation in the bone far more significant injuries can lead to a fracture, or break, of the bone.
I typically use the analogy of a paperclip to illustrate how these injuries happen. Bend the wire of a paperclip back and forth enough occasions and the metal will start off to get warm. That heat is analogous to a mild bony pressure damage. Keep bending the paperclip, and it will at some point break, significantly like with a tension fracture.
Bony pressure injuries take place in athletes who engage in high volumes of exercising with out permitting ample rest time for the bone to heal among routines. A skier might be more at chance for this variety of injury if his or her diet regime does not supply adequate vitality or nutrition to let the bone to heal correctly. Bony pressure injuries can occur anyplace in the reduce leg, including the two the massive shin bone, or tibia, and the smaller shin bone, or fibula.
The spot of discomfort is often much a lot more focal than in shin splints, with the athlete becoming able to level, with a single finger, to exactly where the discomfort is most intense. Discomfort often worsens with exercise, leading to an athlete to abandon routines or races earlier and earlier as the injury progresses.
Because symptoms can overlap with those of shin splints, an MRI is frequently utilised to distinguish in between the two. Therapy for a bony stress injury calls for rest for the bone. If the bone has fractured in a high-risk spot, even so, surgical treatment could be needed. Instruction through worsening shin pain may lead to a more critical anxiety fracture with a much longer lay-off from skiing, or even a season-ending surgical treatment. It’s crucial to get a diagnosis and total work-up rapidly. If caught early, these injuries can be managed properly and prevented from worsening.
Exertional compartment syndrome is a much less regular result in of shin ache in nordic skiers and can be difficult to diagnose. Compartment syndrome occurs when the muscle tissues increase for the duration of physical exercise, due to elevated blood movement, but the sheath close to the muscle does not stretch adequately, which causes the strain in the muscle compartment to improve.
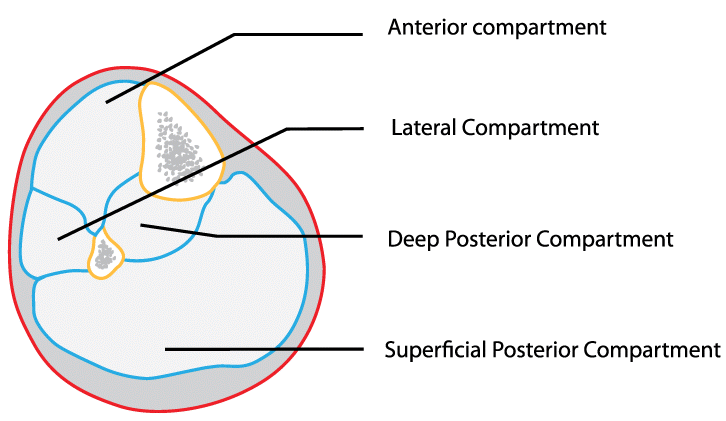
The four muscle compartments in the reduced leg: a single in the front, one particular on the outside, and two in direction of the back.
There are four this kind of compartments in the reduced leg: 1 in the front, one particular on the outdoors, and two in the direction of the back of the lower leg (at appropriate). Athletes with this condition complain of crampy ache in the shin or calf that begins a number of minutes into exercising, continues to worsen, and then swiftly improves soon after they quit working out. This ache is induced by the muscle becoming strangulated as the high stress in the compartment prevents muscle tissue from acquiring enough blood to carry on to perform at a substantial level.
Depending on which compartment or compartments are affected, and if these compartments incorporate nerves, athletes can also really feel tingling or numbness related with the ache. They might even knowledge a sensation that the foot or ankle are weak, triggering the skier to more frequently catch their tips in the snow. A sports medication doctor could purchase an X-ray or MRI to rule out other leads to of ache, and may also recommend a special check to measure the pressure in the compartments prior to and right after workout. Compartment stress testing can be unpleasant, nevertheless, and a diagnosis of compartment syndrome can often be reached with no it.
Most compartment syndrome can be handled non-surgically with the correct bodily therapy and strategy adjustments, but in some instances, surgically opening the compartments of the reduced leg can be valuable by opening the muscle sheath and allowing the muscle to broaden totally in the course of workout.
Shin splints, bony pressure injuries and exertional compartment syndrome have comparable signs and symptoms, but they demand quite diverse management approaches. Skiers who expertise shin pain that worsens with physical exercise or lasts a lot more than two weeks, despite rest, must right away seek advice from a sports medication doctor who is acquainted with the demands of nordic skiing. Addressing the damage early might avoid a a lot worse injury, and even allow the athlete to proceed skiing at a large level whilst addressing some correctable method, power, or flexibility issues throughout the remainder of the season.
***
About the Writer: Krys Bigosinski, MD., is a sports activities medicine physician in Portland, Maine. He helps supply healthcare coverage for the US Cross Nation Ski Team and is an avid nordic skier. He is also the Associate Plan Director for the Maine Healthcare Center Sports Medication Fellowship.

Krys Bigosinski, MD is a sports medicine doctor in Portland, Maine